Do you think you are safe from fires? It just takes one spark to turn everything into ashes.
Imagine if, last night, you were changing your car oil, and there was a small oil spill, too, but you got tired, left all the things wherever they were, and went to sleep.
In the middle of the night, you wake up to a smoke alarm. Upon your inquiry, you find out that something in your garage sparked a fire, which has spread all over the garage and is uncontrollable.
These are the scenarios that can happen with a Type B fire. If you are unaware of the intensity of Type B fire, how to spot it and avoid fire hazards, this article will help you understand everything you need to know.
What Are Common Characteristics Of A Type B Fire?
Type B fires are caused by flammable liquids and gases, making them significantly different from other fires and more challenging to control. Here are a few key characteristics of fire class type b:
1. Rapid Spread
As mentioned earlier, flammable liquids are the main cause of type B fires. Unlike type A fires, these fires spread more rapidly and end up causing more damage.
A tiny spark can lead to devastating consequences, whether it is a fuel spill in a garage or some cooking oil in the kitchen.
2. High Heat
Another dangerous characteristic of the type b fire class is that they generate high heat from burning the liquid.
This may cause nearby objects to catch rapid fire or, in some cases, lead to explosions when flammable gases or chemicals are involved. The higher the temperature, the more destructive the fire becomes, making it difficult to manage.
3. Ineffectiveness Of Water
People might think water is the solution to all types of fires, but that is not the case. In type B fire, water can make the situation worse.
But why? Water is not soluble in oils, so pouring water on flammable liquids like oil or grease will cause the liquid to spread further instead of getting cleaned, spreading to other areas and creating dire circumstances. In short, water is not your ultimate type B fire extinguisher.
What Are The Most Common Causes Of Type B Fires?
According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the most common cause of Type B fire includes combustible and flammable liquids, tars, petroleum greases, oils, oil-based paints, solvents, lacquers, alcohol, and flammable gases. Let’s have a look at each of the causes in detail:
Flammable Liquids
Flammable liquids are usually the primary cause of type B fire. Here’s a list of some primary liquids that could lead to such fires:
Petroleum-Based Products
Gasoline, diesel, and kerosene are highly flammable liquids, and even small spills or leaks can lead to massive type B fires, especially when they come in contact with other flammable materials, including solids or liquids.
Alcohols
Laboratories usually contain alcohol-based products like ethanol, methanol, or some cleaning agents that can be ignited easily. If these products are not stored accurately or carefully, they can cause type B fires that can also spread to nearby substances.
Oil Based Paints and Solvents
Oil-based paints contain volatile compounds that, if exposed to heat or flames, can ignite, resulting in Type B fire. Solvents and paint thinners must be stored with care, as they can lead to fast-spreading fires that are hard to control.
Flammable Gases
1. Propane and Butane
Propane and butane are two of the most commonly found gases in kitchens for cooking or industrial equipment. If they leak from damaged lines or appliances, they can cause explosions and type B fires.
2.Natural Gas
Natural gas is used for cooking and heating; however, mishandling or leaks could lead to bigger disasters. For instance, if you leave the stone on after cooking, and when you turn the kitchen lights on, the spark could cause a massive explosion.
Spills and Vapors
Even if the spill is minor, flammable liquids produce vapors that travel through the air and ignite as soon as they come in contact with heat or flame. Accumulated vapors can also lead to flash fires, spreading the fire much faster.
Ignition Sources
The presence of an ignition source is the final trigger for a Type B fire, most times. Familiar ignition sources include:
1. Open Flames
Matches, candles, lighters, or stoves with open flames are some of the significant causes of type B fire when they come in contact with flammable liquids. Just a tiny spark can set off a massive fire in seconds.
2. Electricity Sparks
Certain industrial or household machinery, such as gas pumps or other electrical equipment, can produce sparks that ignite nearby flammable liquids or gases.
3. Hot Surfaces
If flammable gases or liquids come in prolonged contact with high-temperature equipment, they can lead to an instant fire outbreak.
Improper Storage and Handling
It is best to handle and store flammable substances with careful consideration because minor ignorance can lead to massive destruction.
Heat Proximity
Storing flammable substances near heat sources is one of the worst things you can do. If they come into prolonged contact with the heat, a major fire can erupt.
Unsealed Containers
The vapors can accumulate or spread to nearby spaces if the flammable substances are not stored in properly sealed containers. As soon as they come in contact with the ignition source, they can ignite a fire.
Human Error
Smoking Near Flammables
“No Smoking,” is a common sign at gas stations because the containers have flammable liquids and gases that can spark by a single cigarette. Thus, smoking around the flammable liquids is prohibited to avoid fires.
Equipment Malfunctions
Neglecting malfunctioning equipment for a long time can be dangerous. Equipment like gas stoves, pipelines, industrial machinery, or even a leaked refrigerator can lead to fire outbreaks.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Dealing with a Type B Fire?
Always be careful when handling flammable liquids because minor carelessness can lead to irreversible damage and consequences.
Proper Extinguisher Selection
The foremost vital way to save yourself and your surroundings is by knowing the correct type of fire extinguisher to use for type B fires. Type B fire extinguishers are used for putting out fires caused by flammable liquids. If you are unaware of handling fire extinguishers, get exclusive fire training from Coggno.
How to Choose Right Type of Fire Extinguisher
Here’s a list of extinguishers you might need:
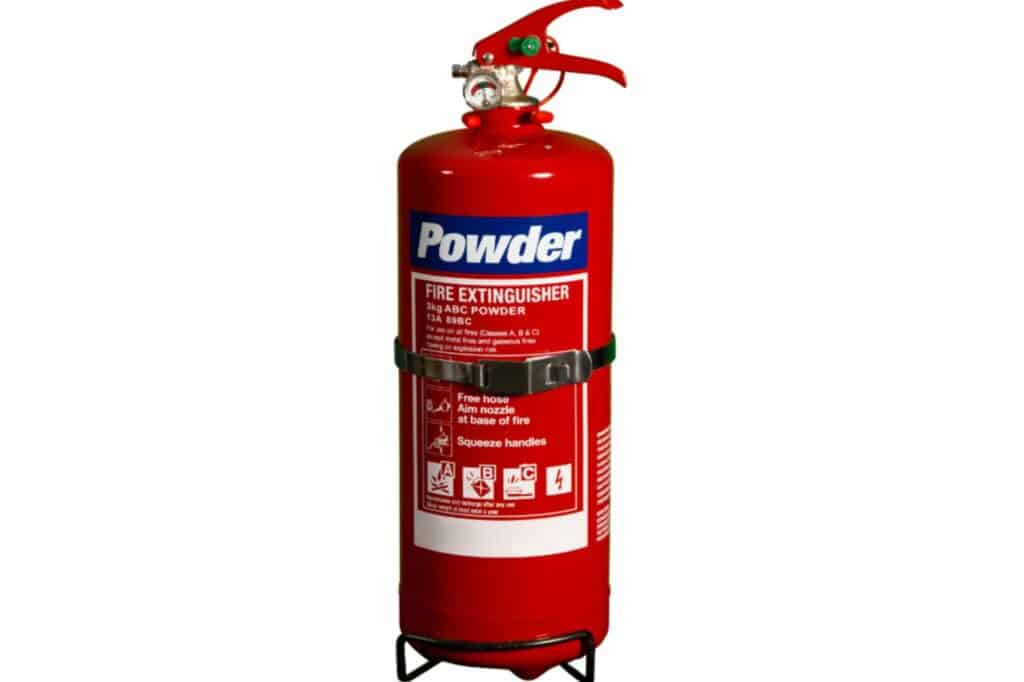
Dry Powder Extinguishers
Dry powder extinguishers, labeled blue, are made for Type B, C, and D fires. They smother the flames, preventing them from spreading to nearby spaces.
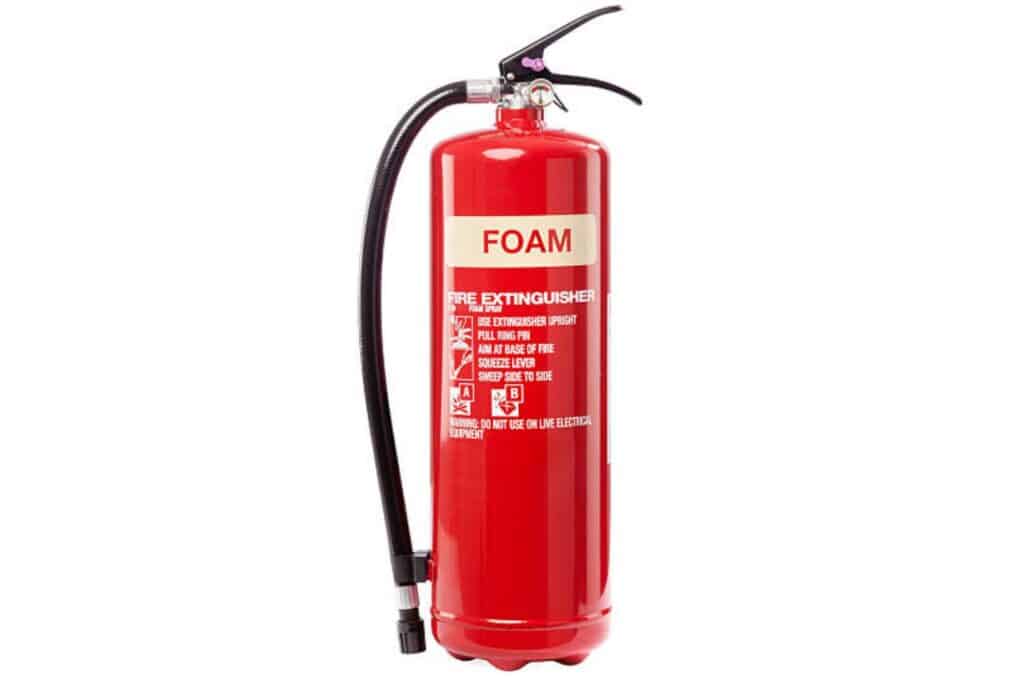
Foam Extinguishers
A foam extinguisher, labeled cream-colored, is ideal for putting out type A and B fires. The foam creates a barrier between the fuel and the oxygen in the air, suppressing the fire and ultimately putting it out.
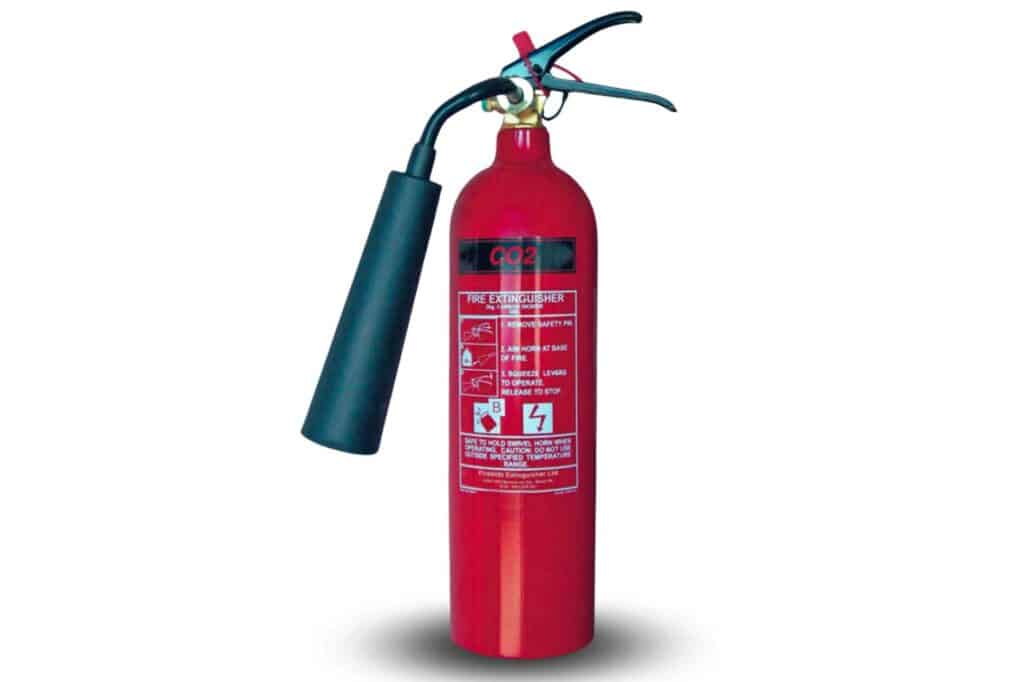
Carbon Dioxide Extinguishers (CO2)
Carbon Dioxide extinguishers are identified with a black label, which is perfect for Type B fires involving sources like flammable liquids and gases.
The CO2 is blasted into the fire that has been reacting with oxygen and replaces the oxygen, resulting in the cooling of the fire.
Preventative Measures
To prevent type B fires, following all the SOPs to store flammable substances carefully is crucial.
Store Flammable Liquids Safely
Always store flammable liquids in approved containers and keep them away from heat or any other source that could ignite the fire.
Avoid Storing Excess Liquid
Even if you get the liquid at a discounted rate, only buy and store what you need. The more flammable liquid you have, the more significant the risk of its spill and fire.
Use Steel Storage Cabinets
Using steel containers or cabinets to store your flammable liquids can add to your peace of mind, ensuring safety. Steel provides extra protection and reduces the chances of fire spreading if something goes south.
Conclusion
The proper knowledge and preparation can reduce the risk of type B fires, and you can get the right kind of fire training and the appropriate extinguisher.
Coggno offers expert fire extinguisher training that teaches you how to handle type B fires. So, sign up and start your training now!